Appendix:
- Introduction
- Macronutrients: The Building Blocks of Nutrition
- Micronutrients: Essential Vitamins and Minerals
- The Importance of Meal Timing and Portion Control
- Hydration and Its Role in Healthy Eating
- Creating Sustainable, Long-Term Habits
- Conclusion
Introduction
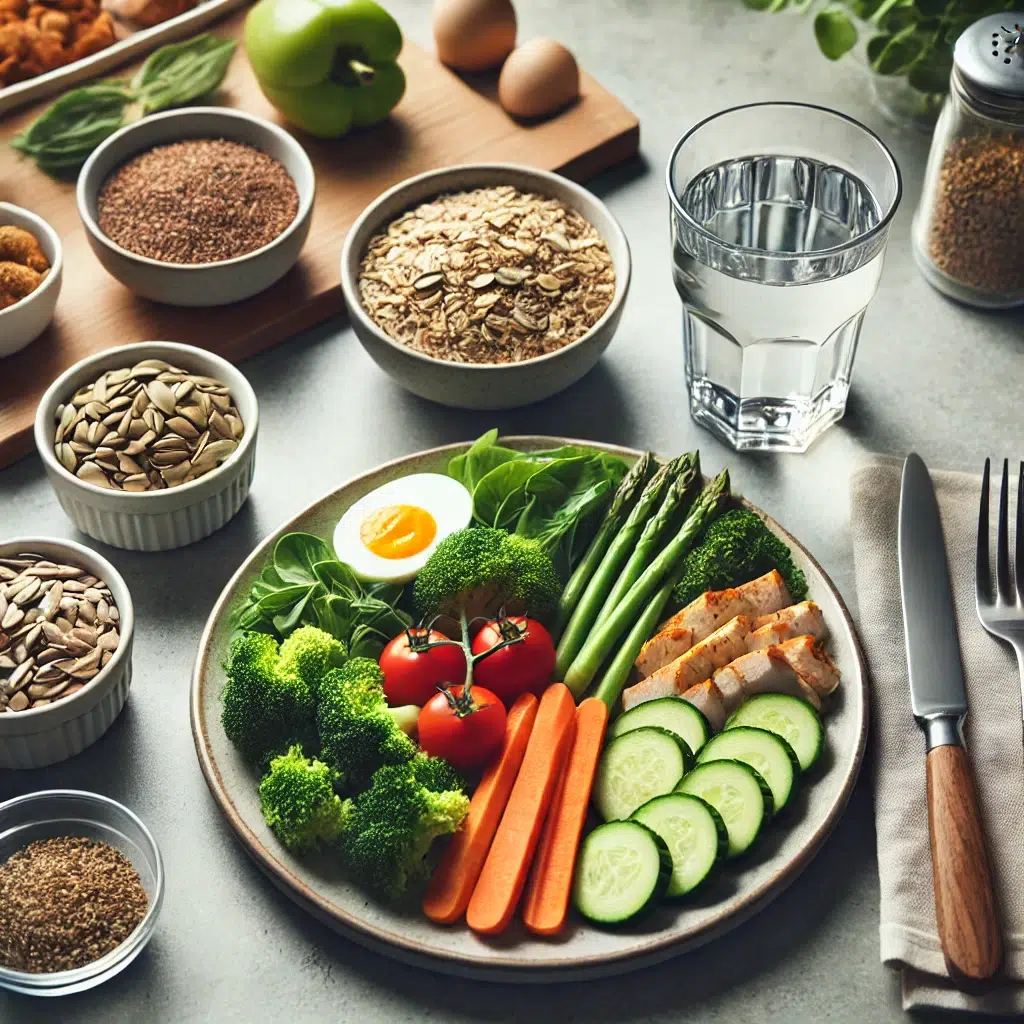
When it comes to healthy nutrition and eating habits, there is a lot of information out there, but it’s important to focus on the fundamentals. Eating a balanced diet, making sure to get the right amount of nutrients, and developing sustainable habits are all critical to achieving long-term health. In this guide, we will explore the most important factors to consider when developing healthy nutrition and eating habits.
Macronutrients: The Building Blocks of Nutrition
Macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and they are essential for energy and bodily functions. Understanding the role of each macronutrient can help you create a well-balanced diet:
1. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body's primary energy source. They can be classified into two types: complex carbohydrates (found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables) and simple carbohydrates (found in sugary foods and drinks). Opting for complex carbohydrates helps regulate blood sugar levels and provides a steady source of energy throughout the day.
2. Proteins
Proteins are critical for muscle repair, immune function, and the production of enzymes and hormones. Lean proteins like chicken, fish, beans, and tofu should be prioritized to support a healthy diet.
3. Fats
Fats are necessary for brain function, hormone production, and the absorption of certain vitamins. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, should be included in your diet, while trans fats and saturated fats should be limited.
Micronutrients: Essential Vitamins and Minerals
While macronutrients are essential for energy, micronutrients are just as important for overall health. These include vitamins and minerals that support various functions in the body:
| Nutrient | Role | Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | Bone health, immune function | Fortified foods, sunlight, fatty fish |
| Iron | Oxygen transport, energy production | Red meat, spinach, lentils |
| Calcium | Bone health, nerve function | Dairy products, leafy greens, fortified foods |
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant, immune support | Citrus fruits, bell peppers, strawberries |
Micronutrient deficiencies can lead to health problems, so it's important to eat a varied diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
The Importance of Meal Timing and Portion Control
Beyond what you eat, when and how much you eat are also important considerations for maintaining healthy nutrition and eating habits.
1. Meal Timing
Eating regular meals helps keep your metabolism active and maintains consistent energy levels throughout the day. Skipping meals can lead to overeating later and negatively affect your blood sugar levels.
2. Portion Control
Managing portion sizes is crucial for preventing overeating and maintaining a healthy weight. A useful tip is to follow the plate method, where half your plate is filled with vegetables, a quarter with lean protein, and a quarter with whole grains. Learning to recognize when you're full can help prevent the tendency to eat beyond your body’s energy needs.
Hydration and Its Role in Healthy Eating
While not technically a nutrient, water is essential for life and plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and temperature regulation. Staying properly hydrated can also help control hunger, as thirst is often mistaken for hunger.
The Institute of Medicine recommends about 3.7 liters (13 cups) of water per day for men and 2.7 liters (9 cups) per day for women, though this can vary based on activity level and climate.
Creating Sustainable, Long-Term Habits
Many people adopt strict diets only to abandon them weeks later due to their unsustainability. The key to healthy eating is creating habits that you can maintain long-term. Here are a few strategies:
1. Start Small
Begin by making small changes, such as adding an extra serving of vegetables to your dinner or switching from white bread to whole grain. Over time, these small habits will become second nature.
2. Seek Professional Guidance
Working with a professional in nutrition coaching can help you develop personalized strategies to achieve your goals while providing support and accountability.
3. Mindful Eating
Practice mindful eating by paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, and eating slowly to savor each bite. This helps prevent overeating and encourages better food choices.
Conclusion
Developing healthy nutrition and eating habits is essential for long-term well-being. By focusing on a balanced intake of macronutrients, ensuring you're getting enough micronutrients, managing portion sizes, staying hydrated, and creating sustainable habits, you can improve both your physical and mental health. Don't hesitate to seek professional help from a nutrition coaching service to support you in this journey.


No Comments.